√99以上 atmosphere diagram greenhouse gases 339877
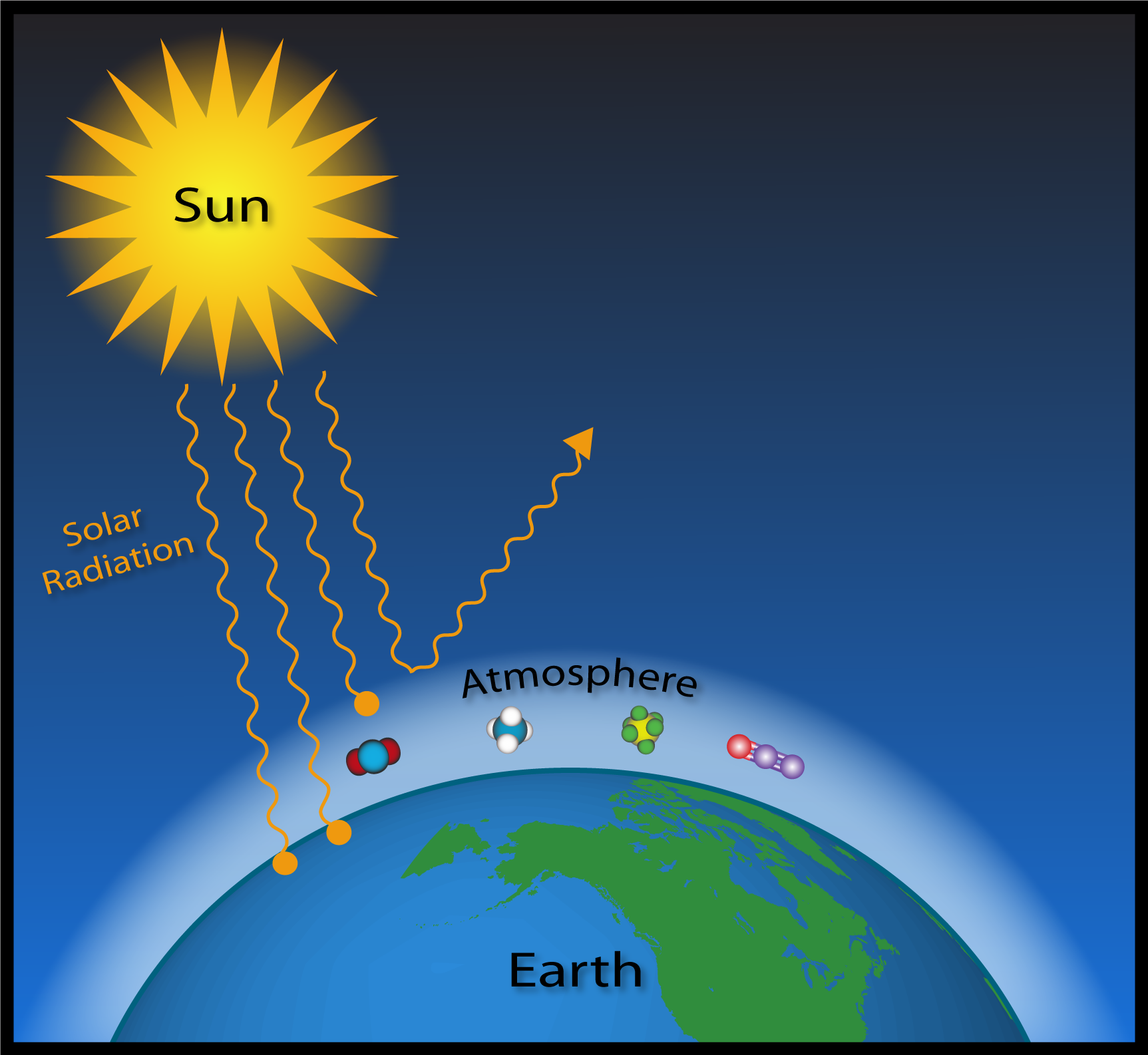
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, including water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, act to make the surface much warmer than this because they absorb and emit heat energy in all directions (including downwards), keeping Earth's surface and lower atmosphere warm Figure B1 Without this greenhouse effect, life as we know it could not have evolved onFluorinated Gases (HFCs, PFCs, SF 6) Fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than the other greenhouse gases, but what they lack in volume they can make up in potency and long lifespans in the atmosphere, ranging from 1270 years for HFCs to ,000 years for PFCs and about 3,0 years for SF6Gases of the Atmosphere Match each layer with its description _____ exosphere _____ ionosphere _____ mesosphere _____ stratosphere _____ thermosphere _____ troposphere A closest to Earth, where

The Science Hoosier Environmental Council
Atmosphere diagram greenhouse gases
Atmosphere diagram greenhouse gases-Atmospheric gases Water vapor is the Earth's most important natural greenhouse gas Water vapor and clouds cause most of the Earth's natural greenhouse effect and account for about 90% of the total heatretaining capacity of the atmosphere Greenhouse gases can also reabsorb solar radiation reflected or reemitted from Earth's surface,However, the actual contribution of a greenhouse gas to atmospheric warming depends not only on its GWP, but also on its concentration At present, the concentrations of halogenated gases in the atmosphere are low and their combined radiative forcing is only about onefifth that of CO 2 Because of overlapping absorptions, total radiative




Igcse Biology 17 4 15 Understand How An Increase In Greenhouse Gases Results In An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And That This May Lead To Global Warming And Its Consequences
Media in category Atmospheric carbon dioxide The following 79 files are in this category, out of 79 total 1705 Climate spiral atmospheric CO2 concentration 1958 screenshot Ed Hawkinspng 691 ×The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), ozone (O3), and fluorinated gasesThe greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Scientists have determined that carbon dioxide's warming effect helps stabilize Earth's atmosphere Remove carbon dioxide, and the terrestrial greenhouse
242 Atmospheric Chemistry and Greenhouse Gases Model calculations of the abundances of the primary greenhouse gases by year 2100 vary considerably across the SRES scenarios in general A1B, A1T, and B1 have the smallest increases of emissions and burdens;Greenhouse gases diagrams • Where do Greenhouse Gases Come From handouts • Greenhouse Gas Emissions Diagram handouts • Colored pencils National Science Education Standards D1h The atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen, oxygen, and trace gases that include water vapor D1j Living organisms have played many roles in the Earth system including affecting the composition of the atmosphereIf there was no ozone gas in the atmosphere, there would not have been existence of living beings and plants on the earth surface (B) Water vapour Gaseous form of water persent in the atmosphere is called water vapour Water vapour present in the atmosphere has made life possible on the earth Water vapour is the source of all kinds of precipitation Its maximum amount in the atmosphere
This diagram shows that the array of radiation, often called the electromagnetic spectrum, varies from the shortest wavelength gamma rays to the longest radio waves Each one of these types of radiation travels through a vacuum at the same speed of light, however, each type of radiation has its own wavelength and frequency Moreover, and this is very important, each packet of radiationEPA has two key programs that provide data on greenhouse gas emissions in the United States the Inventory of US Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Sinks and the Greenhouse Gas Reporting Program The programs are complementary, providing both a higherlevel perspective on the nation's total emissions and detailed information about the sources and types of emissions from individual facilities The data in EPA's US Greenhouse GasCarbon dioxide (CO 2) is the primary greenhouse gas emitted through human activities In 19, CO 2 accounted for about 80 percent of all US greenhouse gas emissions from human activities Carbon dioxide is naturally present in the atmosphere as part of the Earth's carbon cycle (the natural circulation of carbon among the atmosphere, oceans, soil, plants, and




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate
Carbon dioxide and methane (CH4) are two types of greenhouse gases that trap energy from the Sun in the atmosphere, which causes the planet to warm Without any greenhouse gases, the Earth would be too cold to sustain life at current levels, but with the current rapid increase of greenhouse gases, the climate is warming too much Humancaused carbon emissions haveNitrous oxide, N 2 O;Greenhouse Gases The three most common types of greenhouse gases are Carbon Dioxide (CO 2) Carbon dioxide enters the atmosphere through the burning of fossil fuels (oil, natural gas, and coal), solid waste, trees and wood products, and as a result of other chemical reactions such as making cementCarbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and stored when it is absorbed




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com



Greenhouse Gases
CFCs (chlorofluorocarbons) The greenhouseThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphereGreenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gases Greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto Earth's surface, and then the gases, such as ozone,There are many greenhouse gases but these are some of the most important water vapour, H 2 O;




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download
SF 6 does not have a sink, due to its inert properties, so measuring SF 6 has another purpose as a tracer gasThe Carbon Cycle Greenhouse Gases (CCGG) research area operates the Global Greenhouse Gas Reference Network, measuring the atmospheric distribution and trends of the three main longterm drivers of climate change, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), and nitrous oxide (N 2 O), as well as carbon monoxide (CO) which is an important indicator of air pollutionThe presence of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, however, changes the radiation balance Heat radiation (infrared) emitted by the Earth is concentrated at long wavelengths and is strongly absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, such as water vapour, carbon dioxide and methane As a result, the surface temperature of the globe is around 15 °C on average, 33 °C
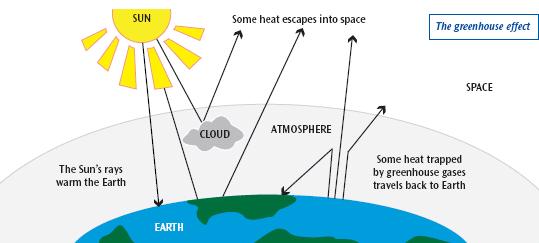



What Is Climate Change And How Will It Affect The Uk Bradford Council




Theme 1 Greenhouse Gases And The Oceans Solas Int
This diagram of the fast carbon cycle shows the movement of carbon between land, atmosphere, and oceans Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, and red are human contributions in gigatons of carbon per year White numbers indicate stored carbon Diagram adapted from US DOE, Biological and Environmental Research Information System) Over the long term, the carbonThe atmosphere of Earth, commonly known as air, is the layer of gases retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphereThe atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing for liquid water to exist on the Earth's surface, absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), andGreenhouse Gas Concentrations Graphing Tool Interactive Data Visualization Tool The Interactive Data Visualization tool gives users a way to explore the abundance of different gases at more than 0 sampling sites around the world You can view graphs showing how the amount of carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, ozone, and various chlorofluorocarbons have changed




Greenhouse Effect Scheme Diagram Showing How Stock Vector Royalty Free




Greenhouse Effect Bioninja
Geschätzte Lesezeit 7 min1 carbon dioxide 2 water vapor Atmosphere Basics KEY wwwHomeEducationResourcescom Layers &Greenhouse Gases Methane, Carbon Dioxide Share of Global GHG Emissions 3% A man scavenges for waste to recycle at a garbage dump in Linfen, China Landfill sites like this produce greenhouse gases because rotting organic waste like food waste emits methane which warms the atmosphere unless it is captured Advanced industrialsed countries




Schematic Of Greenhouse Gas Effect 8 Download Scientific Diagram
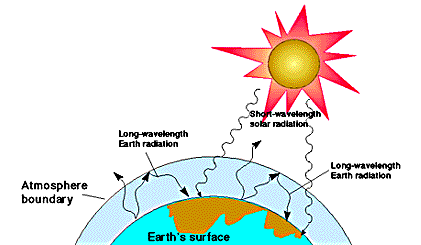



Greenhouse Effect Its Causes And Effect List Of Greenhouse Gases
Composition of Atmosphere – Gases in the Atmosphere The atmospheric composition of gas on Earth is largely conducted by the byproducts of the life that it nurtures Dry air from earth's atmosphere contains 0038% of carbon dioxide, 95% of oxygen, 7808% ofGreenhouse gases in the atmosphere, which leads to changes in climate These changes are affecting many human activities, including agriculture GrEENHOUSE GAS BASICS warming in some places – in the Arctic, for example – is much greater than in others Local changes include shifts in the patterns and severity of rainfall and snowfall, droughts, cloudiness, humidity, and309 KB Play media




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa
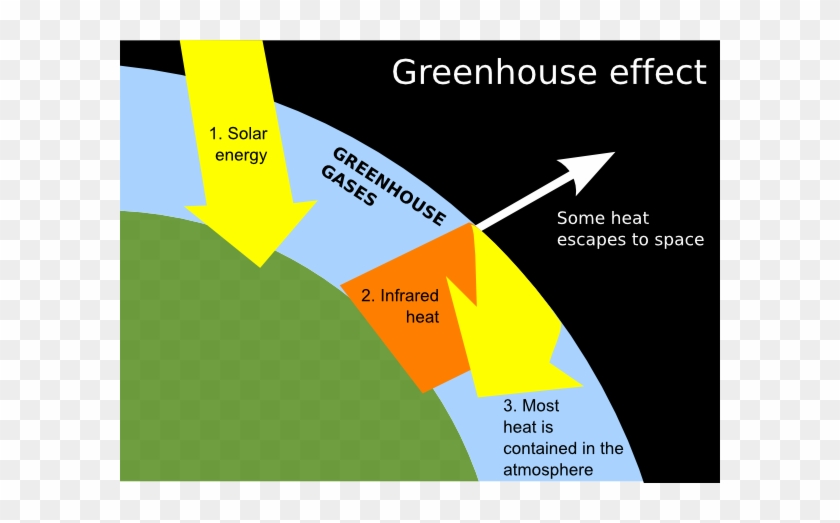



Greenhouse Clip Art At Clker Greenhouse Effect Labelled Diagram Free Transparent Png Clipart Images Download
Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not act as a greenhouse gasGreenhouse gases are gases in Earth's atmosphere that trap heat They let sunlight pass through the atmosphere, but they prevent the heat that the sunlight brings from leaving the atmosphere The main greenhouse gases are Water vapor;474 KB 18 AQAL Group variwide chart Worldwide Co2 emissionsjpg 3,315 ×



Greenhouse Effect Teaching Resources




Igcse Biology 17 4 15 Understand How An Increase In Greenhouse Gases Results In An Enhanced Greenhouse Effect And That This May Lead To Global Warming And Its Consequences
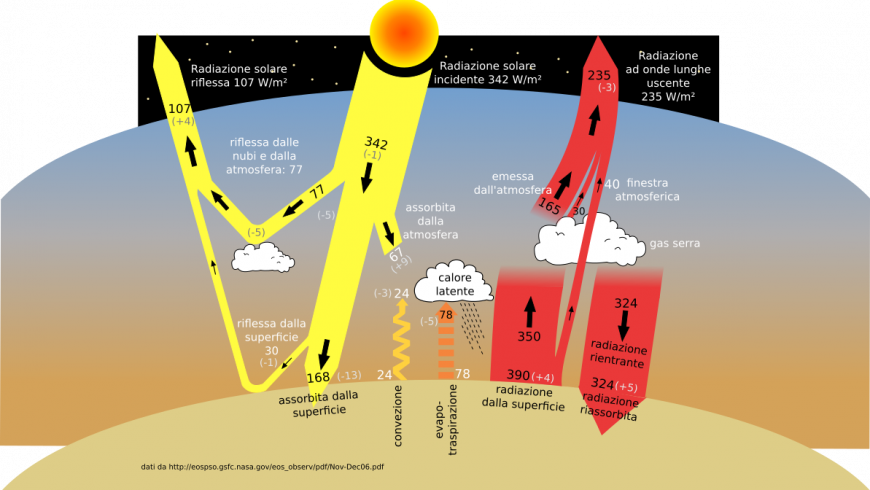
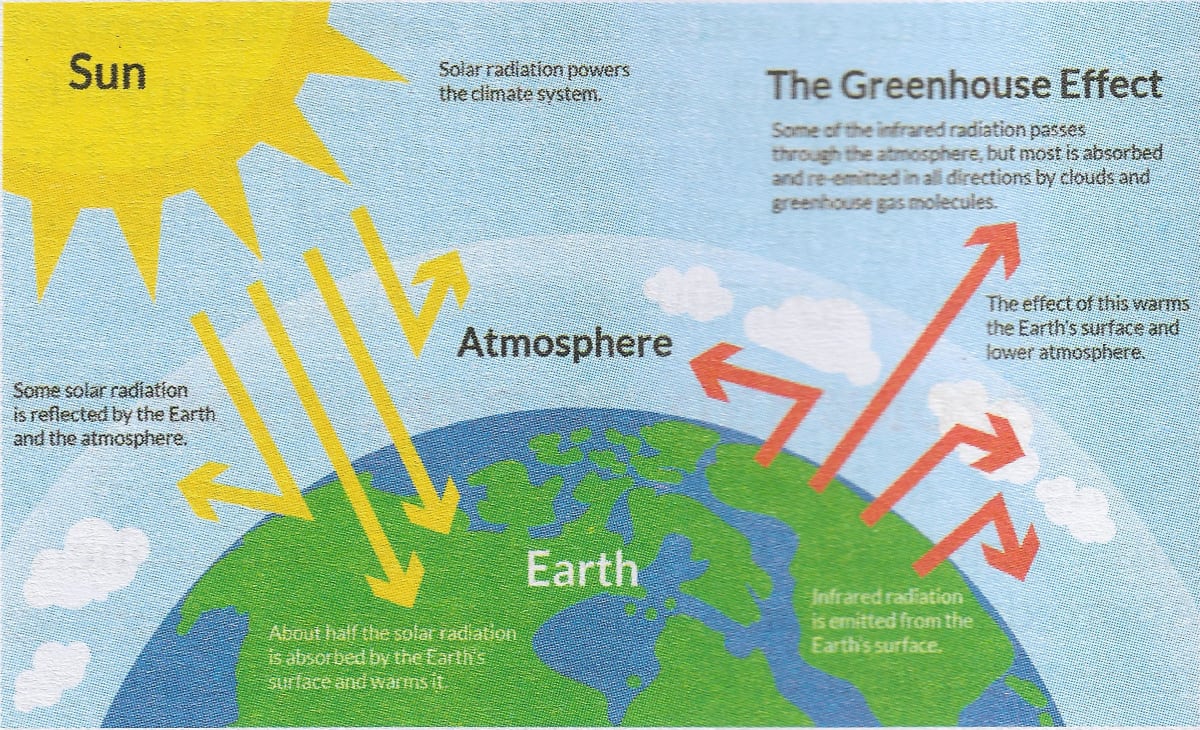
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated gasesQ2 Diagram A shows LW (IR) terrestrial radiation "bouncing off" (or reflecting) the gases in the atmosphere and being sent back to Earth's surface (ie being reflected back to the surface by the gases without being absorbed by them) Is this an accurate depiction of how the Greenhouse Effect works?A diagram, answer opinion questions, and perform a skit to understand Earth's energy balance Students will learn that most of the energy on Earth originates from the sun They will also learn what happens to the energy once it reaches Earth's atmosphere Students will be introduced to the concept of greenhouse gases The activity will close with a discussion of natural vs human
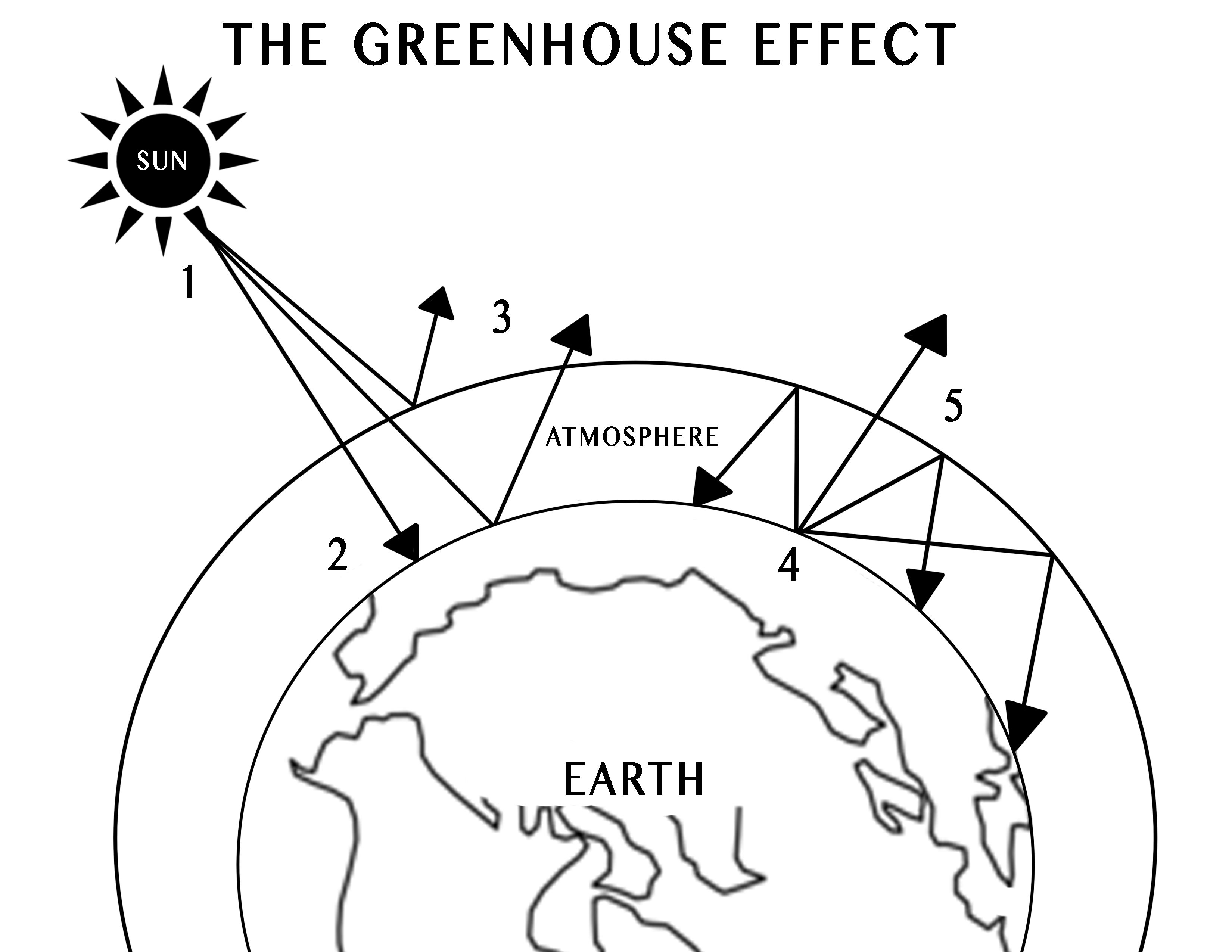



Iv Using Central Ideas About Light And Thermal Phenomena To Explain The Greenhouse Effect Exploring Physical Phenomena




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change
Greenhouse gases come from all sorts of everyday activities, such as using electricity, heating our homes, and driving around town The graph to the right shows which activities produce the most greenhouse gases in the United States These greenhouse gases don't just stay in one place after they're added to the atmosphere As air moves around the world, greenhouse gases become globally mixed, which means the concentration of a greenhouse gasCarbon dioxide, CO 2;Today's atmosphere absorbs more than 3 watts of incoming solar energy over each square meter of Earth's surface According to NOAA's 19 Annual Greenhouse Gas Index (right axis), the combined heating influence of all major greenhouse gases has increased by 45% relative to 1990 Graph by NOAA Climategov based on data from NOAA ESRL



2
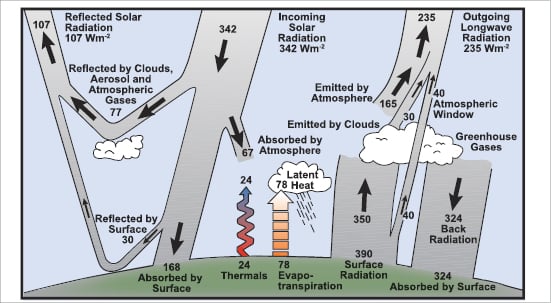



Faq 1 1 Ar4 Wgi Chapter 1 Historical Overview Of Climate Change Science
And A1FI and the largest CH 4 changes from 1998 to 2100 range from −10 to 115%;Greenhouse gases absorb energy transferred as infrared radiation from the Earth's surface release infrared radiation in all directions, which keeps the Earth warm The diagram gives moreVeröffentlicht März 08, 18



Simple




Greenhouse Effect Ck 12 Foundation
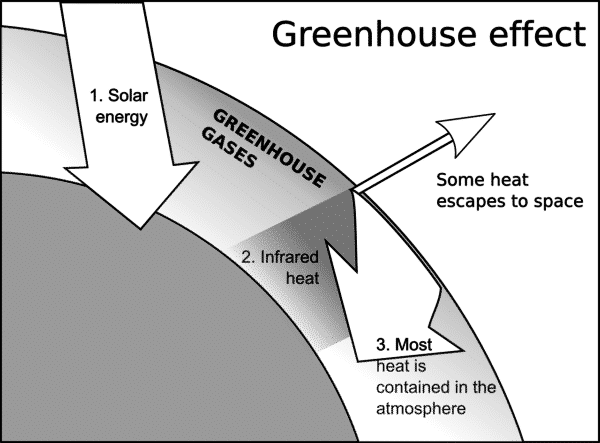
If the atmosphere is like a greenhouse, what parts of it function as the "glass"?Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect The origins of the term greenhouse effect are unclearA greenhouse gas (sometimes abbreviated GHG) is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone Greenhouse gases greatly affect the



Shs Aice Environmental Management 4 3 2 The Atmosphere Kq3 Greenhouse Gases And Climate Change
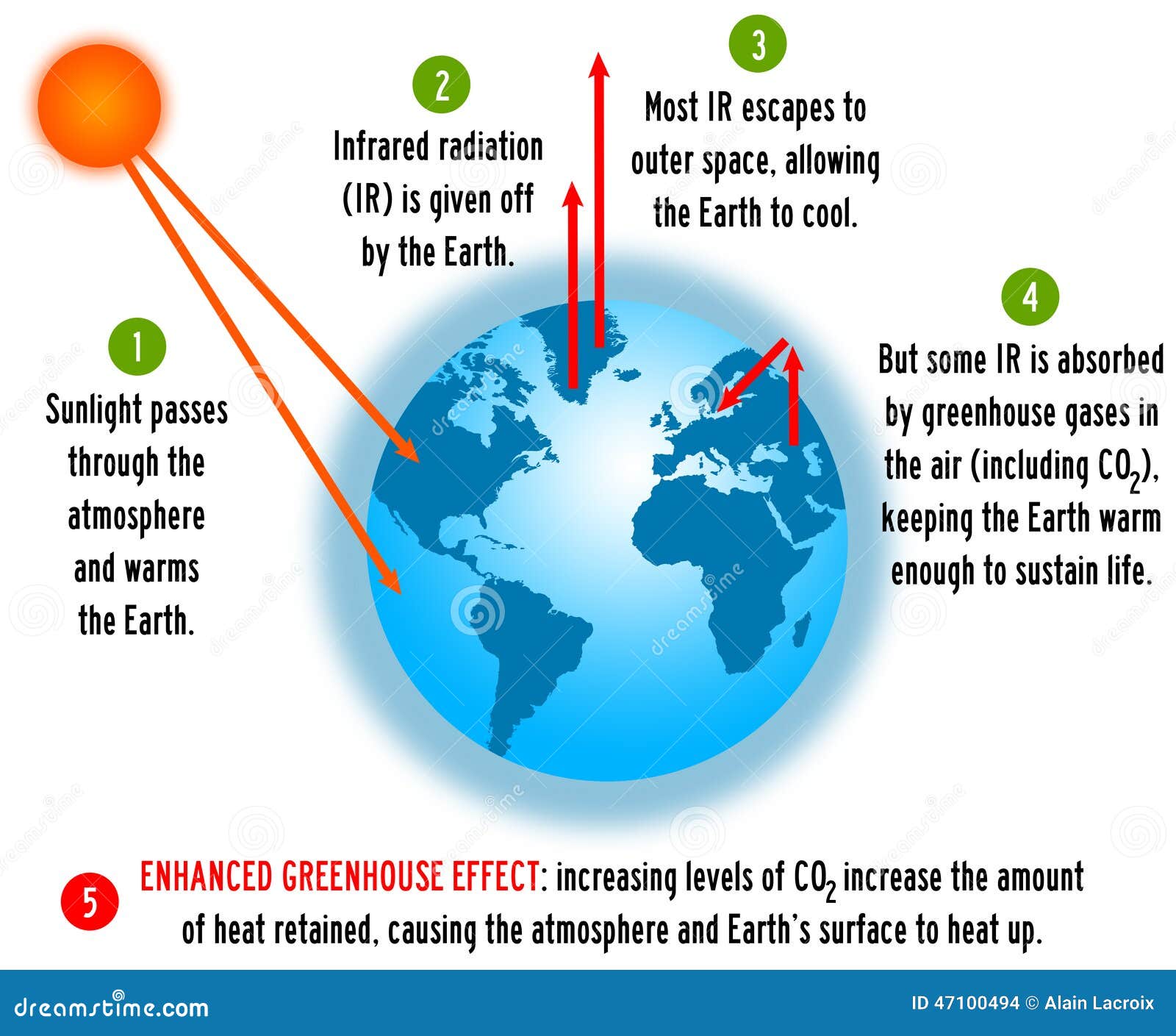



Greenhouse Effect Stock Illustration Illustration Of Global
Important Greenhouse Gases (concentrations in parts per million volume) water vapor 0140,000 carbon dioxide 370 methane 17 nitrous oxide 03 ozone 001 chlorofluorocarbons ~ A greenhouse gas is defined as a gas that absorbs significantly the radiation emitted by the Earth and its atmosphere (Infrared, IR, or longwave radiation) Greenhouse Gases (part 1) • CarbonMost Abundant Gases in the Atmosphere GAS Symbol % by volume % in ppm Nitrogen N 2 7808 780,000 Oxygen O 2 95 9,500 Argon Ar 093 9,300 Total = 9996% p 39To prevent severe climate change we need to rapidly reduce global greenhouse gas emissions The world emits around 50 billion tonnes of greenhouse gases each year measured in carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 eq) 1 To figure out how we can most effectively reduce emissions and what emissions can and can't be eliminated with current technologies, we need to first




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Experiment And Lesson For Kids
This chart shows the change in global greenhouse gas emissions over time Greenhouse gases are measured in 'carbon dioxideequivalents' (CO 2 e) Today, we collectively emit around 50 billion tonnes of CO 2 e each year This is more than 40% higher than emissions in 1990, which were around 35 billion tonnesOver time, it leaks into the atmosphere Current concentrations of SF 6 in the atmosphere are small, but SF 6 has a lifetime of 3,000 years, and per kilogram it is 36,000 times more powerful than CO 2 as a greenhouse gas!!The 'greenhouse effect' is the warming of climate that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space Certain gases in the atmosphere resemble glass in a greenhouse, allowing sunlight to pass into the 'greenhouse,' but blocking Earth's heat from escaping into space The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor,




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Stock Vector Image Art Alamy




Greenhouse Effect
The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention (greenhouse effect), and reducing temperature extremes between day and night (the diurnal temperature variation) The common name given to the atmospheric gases used in breathing and photosynthesis is air By volume, dry air contains 7809% nitrogen, 95% oxygen, 093% argon, 0039% carbon dioxide, and small amounts of other gasesAnd N 2O increases from 13




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram
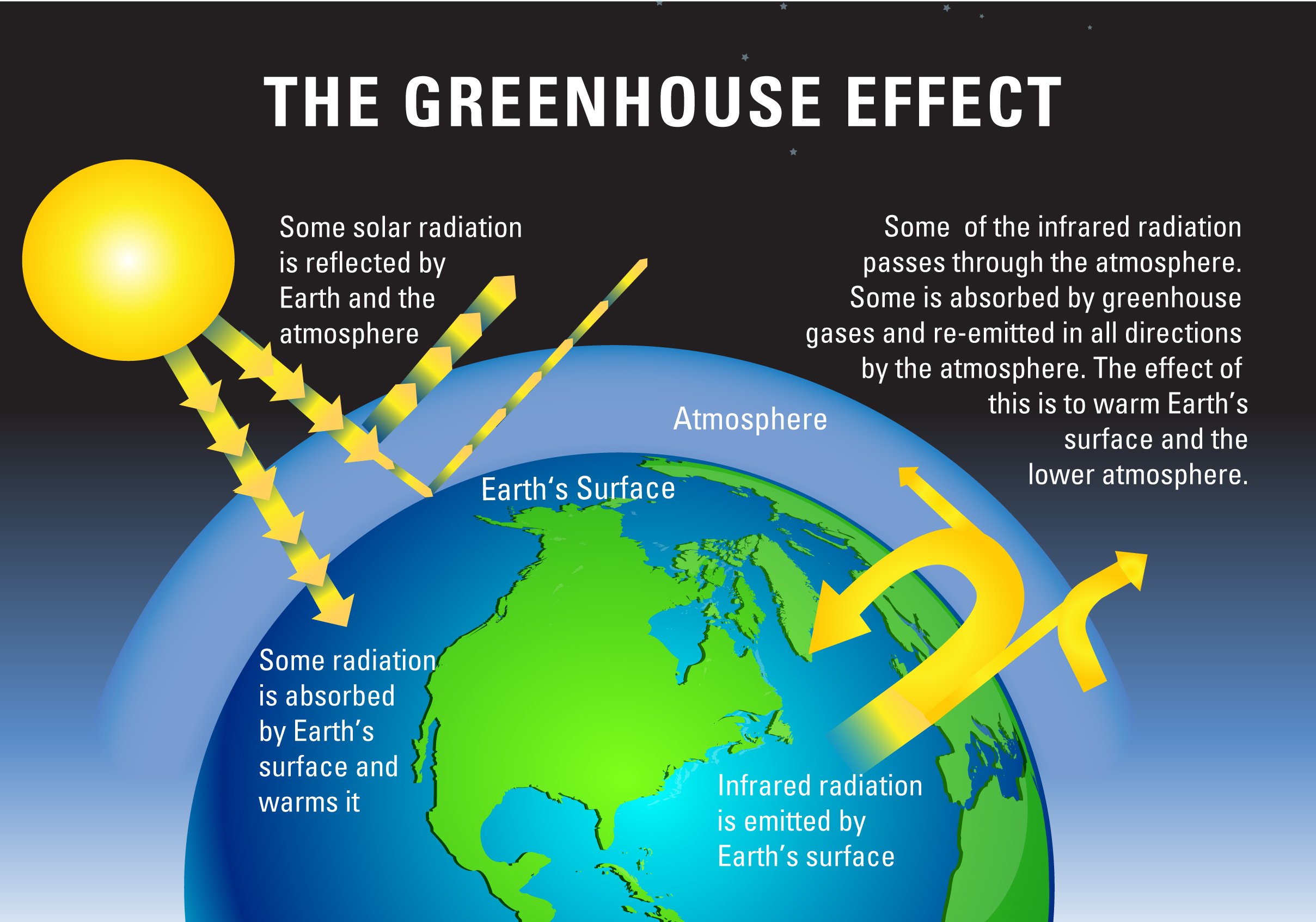



Greenhouse Gases Earth Journalism Network



1




P Fig 3 This Diagram Shows How The Greenhouse Effect Of The Fig 3 This Diagram Shows How The Greenhouse Effect Of The Atmosphere Influencing Our Weather And Climate Image Courtesy Of The Myron B Mbta Mbta Curriculum From Soest




Greenhouse Effect Worksheet
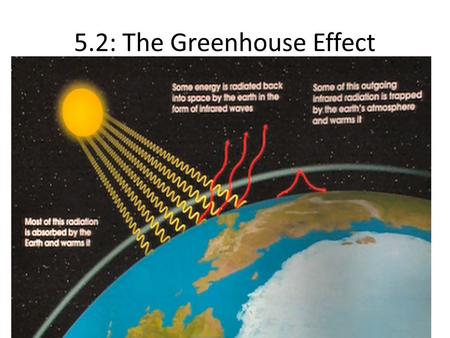



The Greenhouse Effect Draw And Label A Diagram Of The Carbon Cycle Do It Now Ppt Download




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Greenhouse Effect Labeled Greenhouse Effect Diagram Png Image Transparent Png Free Download On Seekpng




File Earth S Greenhouse Effect Us Epa 12 Png Wikimedia Commons



How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut



3



2




How Exactly Does Carbon Dioxide Cause Global Warming You Asked



File Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikimedia Commons




The Greenhouse Effect Diagram Ppt Video Online Download



7 H The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Effect Illustrated




Atmosphere Climate Environment Information Programme



The Following Diagram Shows How Greenhouse Gases Trap Energy From The Sun Ielts Training Tips Ielts Training Ernakulam Kerala India




Co2 The Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming From The Pioneering Work Of Arrhenius And Callendar To Today S Earth System Models Sciencedirect



Greenhouse Gases Teaching Resources
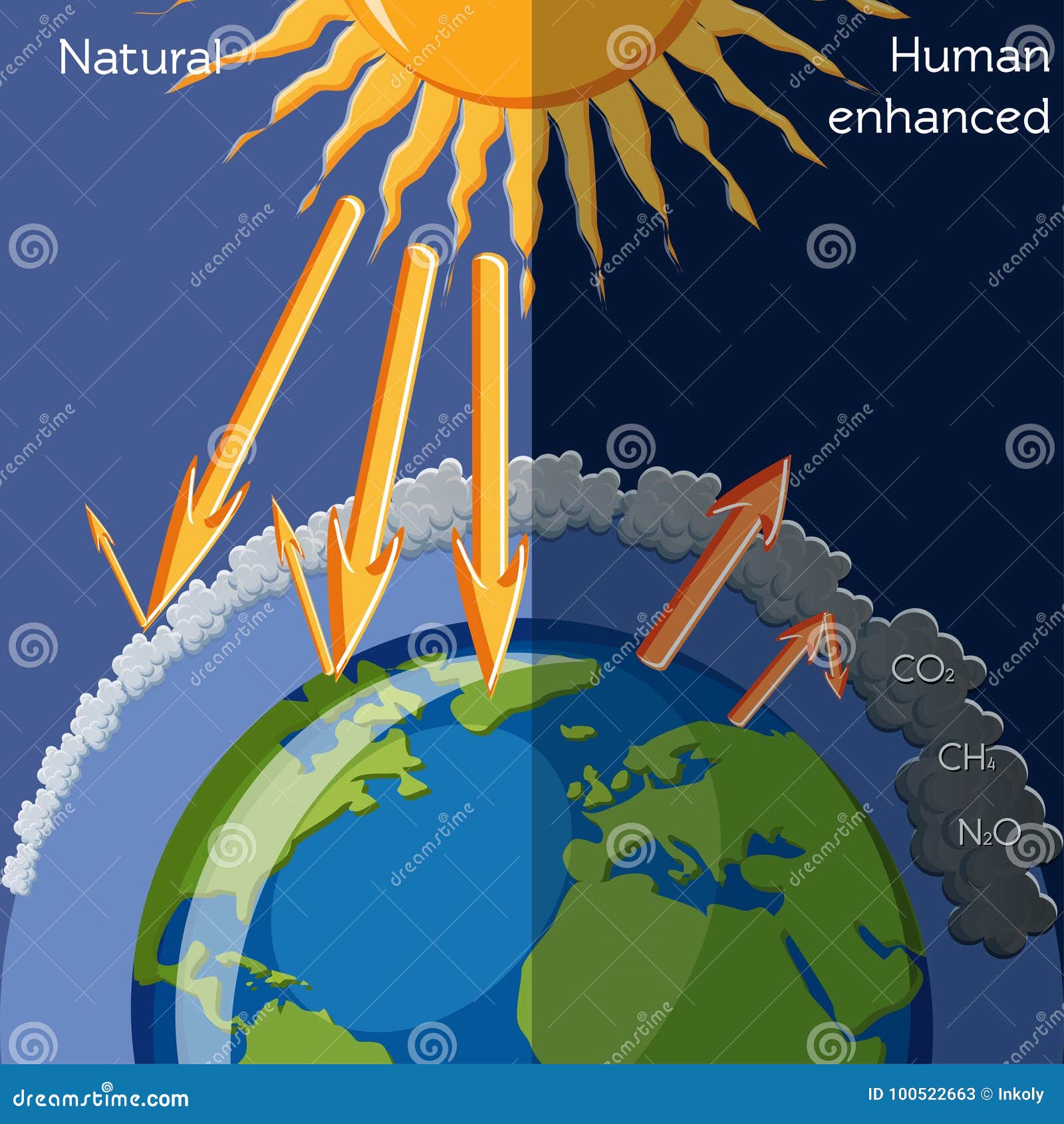



Natural And Human Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Stock Vector Illustration Of Atmosphere Chemical




Greenhouse Effect Diagram Tasmeemme Com
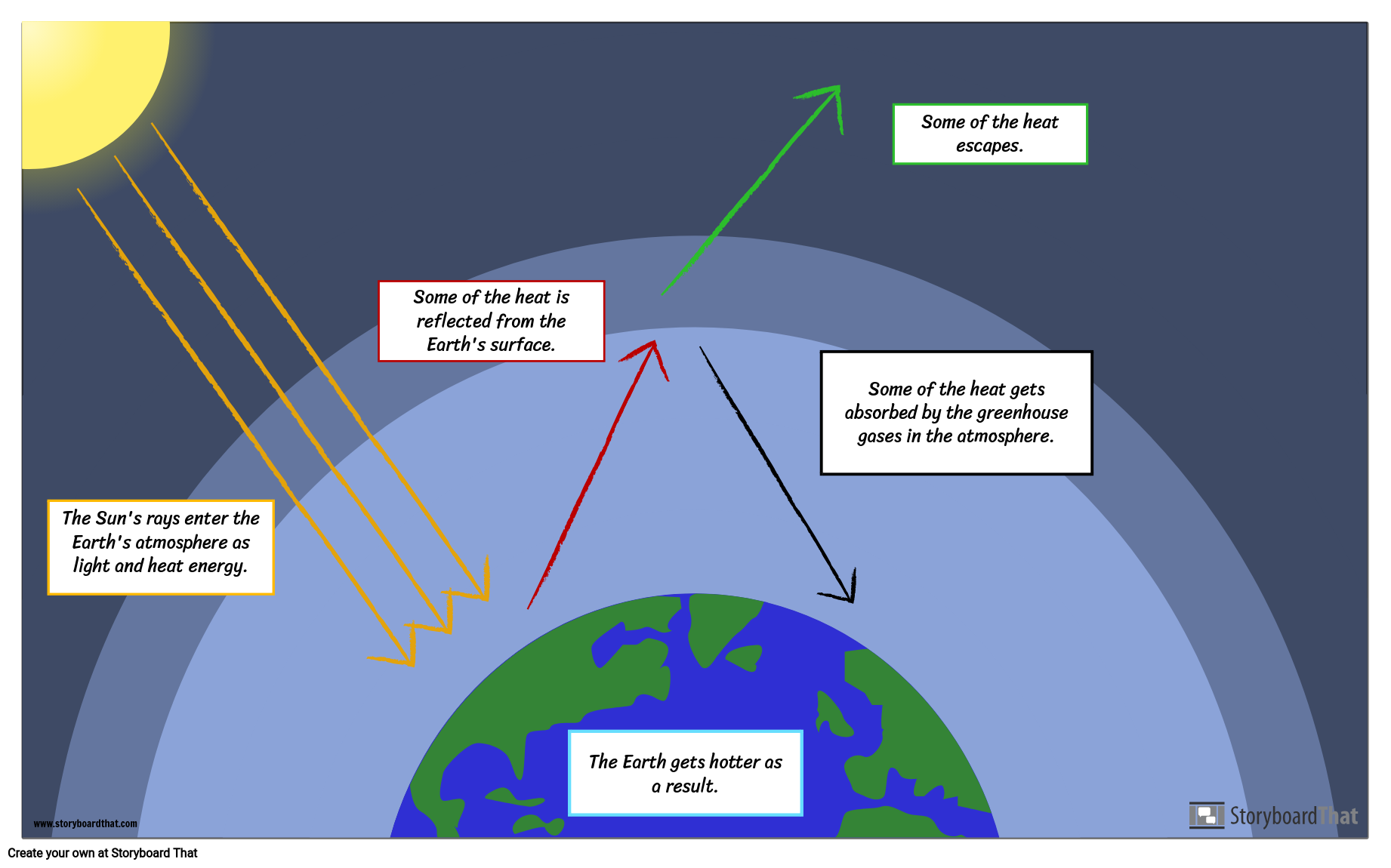



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




A Picture Of Climate Change Is Worth 1 000 Words Greenhouse Gases Climate Change How To Be Outgoing




How To Explain The Greenhouse Effect To Kids With Printables Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases
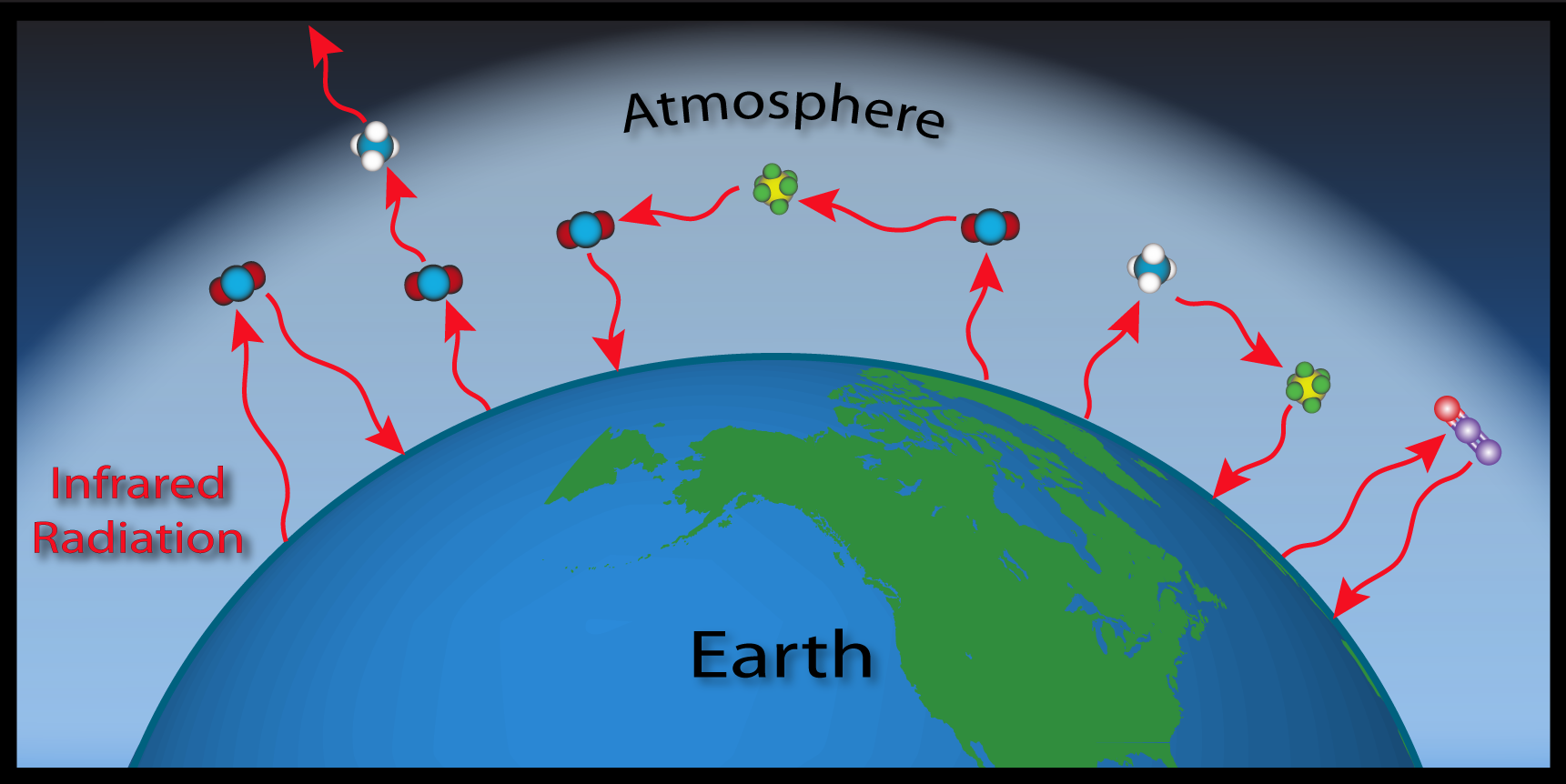



Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Normal Greenhouse Effect Responsible For Maintaining Constant Download Scientific Diagram




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




The Science Hoosier Environmental Council




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
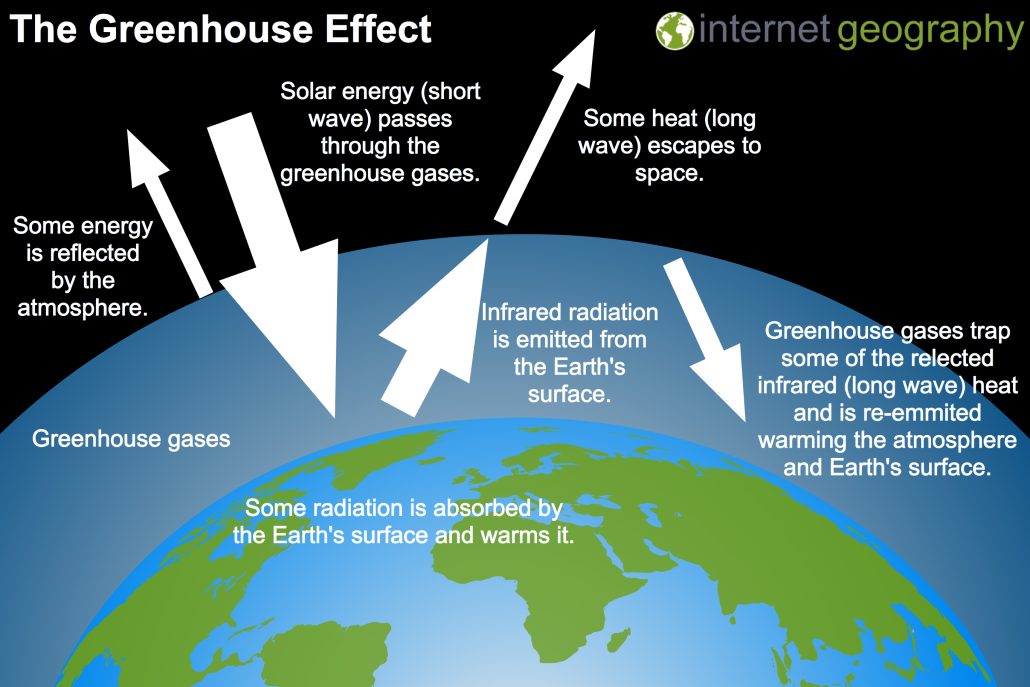



What Causes Climate Change Internet Geography




Practical Guide Greenhouse Gas Emissions Farming For A Better Climate
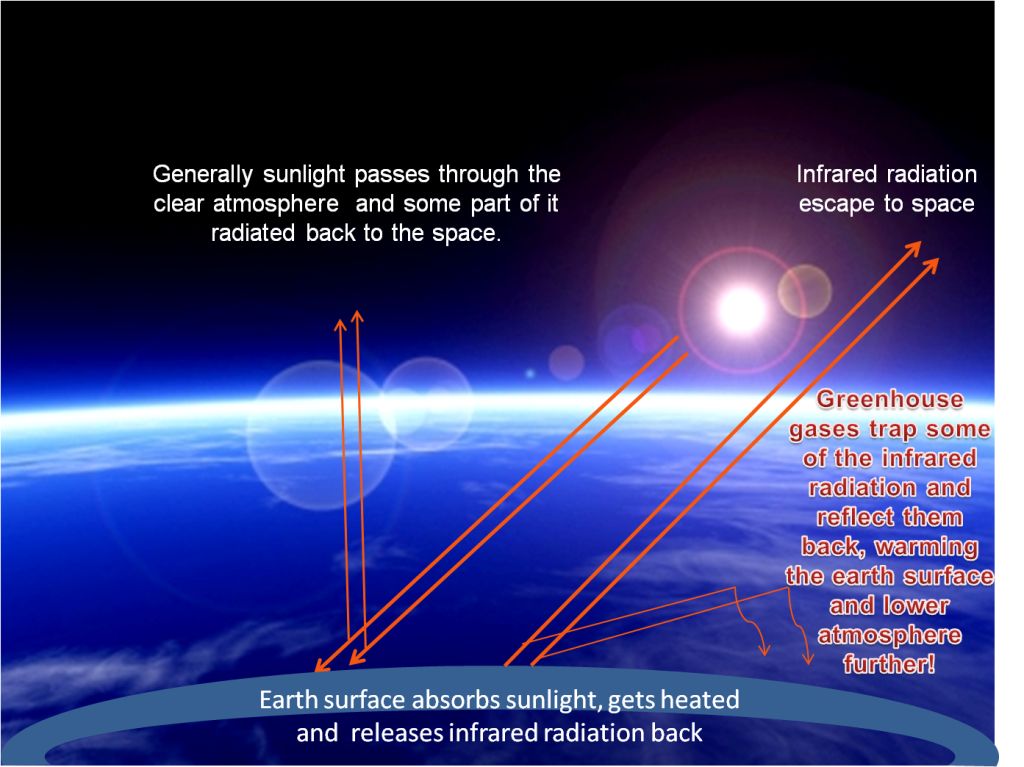



Greenhouse Effect




Solved Activity 2 Show Your Understanding Of The Greenhouse Chegg Com



5 2 The Greenhouse Effect Bioninja




Writing Task 1 The Greenhouse Gaisang S English Study Blog
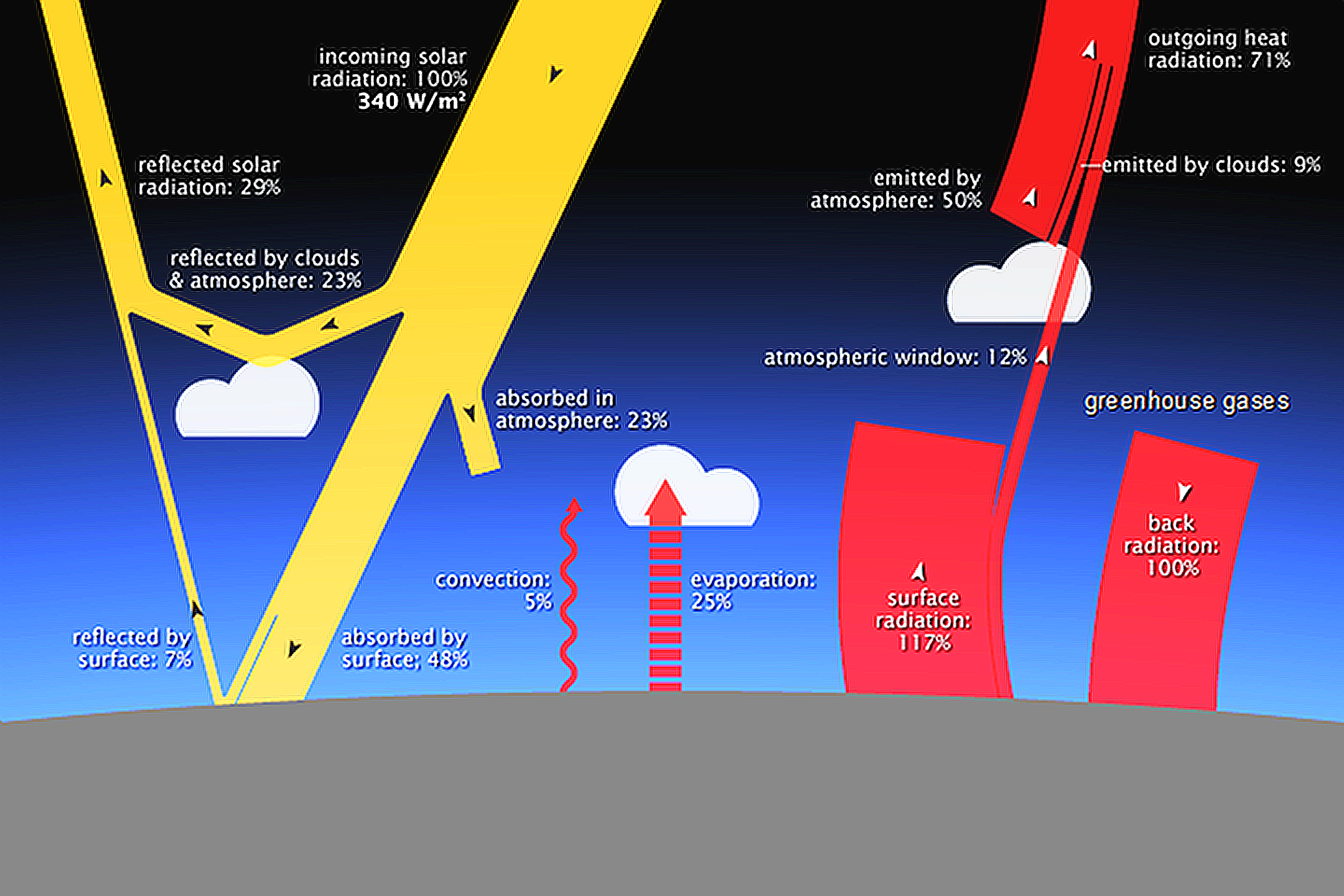



Schools For Future




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
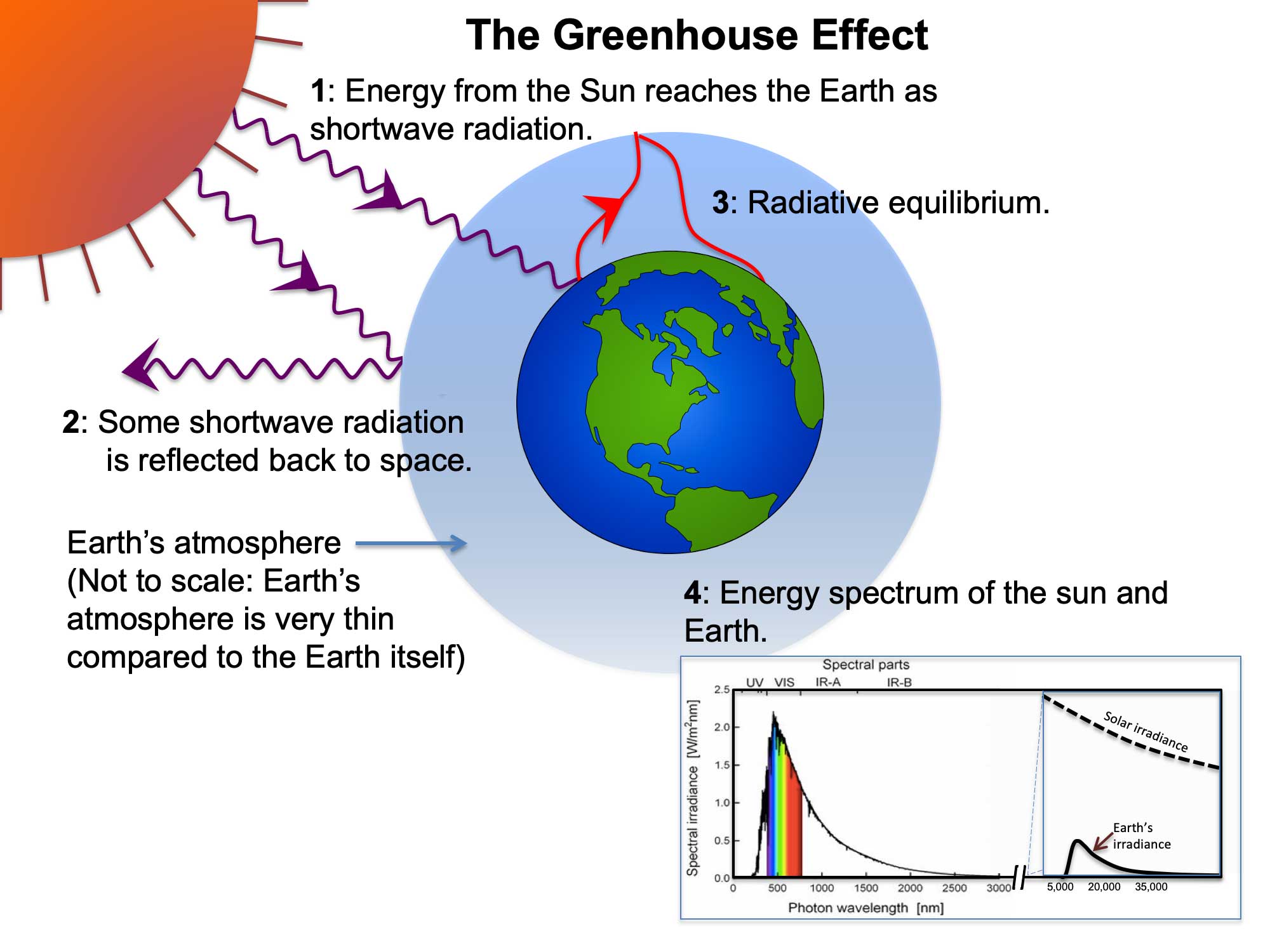



Greenhouse Gases And Global Temperature Earth Home




Greenhouse Gases Copernicus
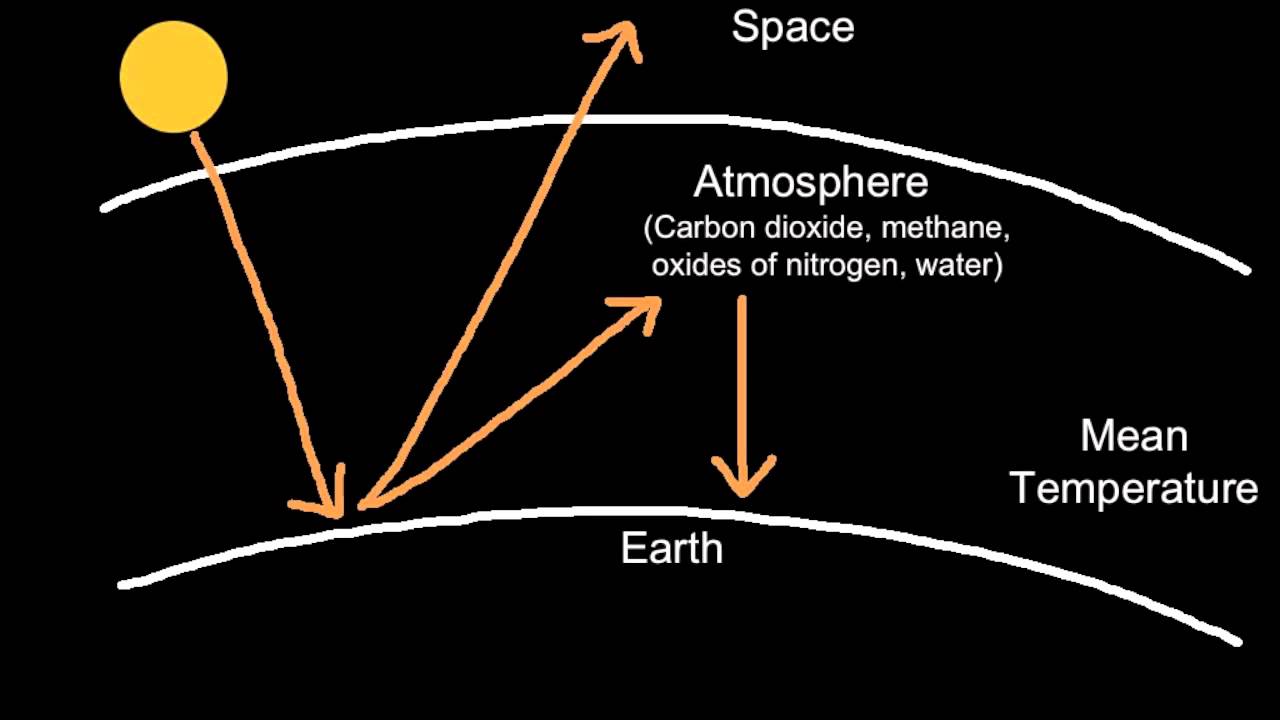



5 2 3 Explain The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Youtube



Greenhouse Gasses Captain John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail U S National Park Service



Greenhouse Gases What Are They What Can We Do To Reduce Emissions




Radiation Budget Diagram For Earth S Atmosphere Ucar Center For Science Education



Greenhouse Gases



Draw A Well Labelled Diagram To Explain The Greenhouse Knowledgeboat



What Is Greenhouse Effect Its Causes Outcome Natural Energy Hub




Greenhouse Effect Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




Greenhouse Atmosphere Let S Heat Things Up Lesson Teachengineering



Global Warming




2 Schematic Of The Greenhouse Effect From 16 Download Scientific Diagram




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids
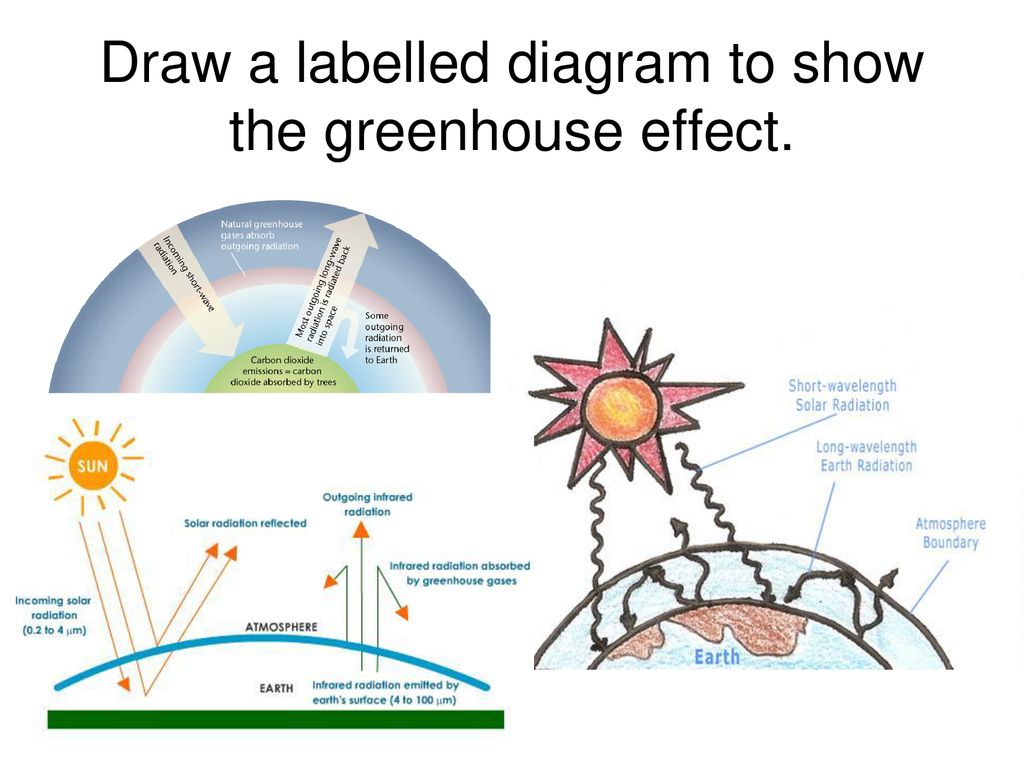



Lesson Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect Kids Environment Kids Health National Institute Of Environmental Health Sciences




Federation Of Maori Authorities Kia Ora Whanau What Are Greenhouse Gases Or Ghg For Short Earth S Atmosphere Is A Mix Of Gases Water Vapour And Particles That Constantly Mix And Mingle




Short Answer Question Explain Greenhouse Effect With The Help Of Diagram Snapsolve



Greenhouse Gases Effect On The Climate And Climate Change




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock
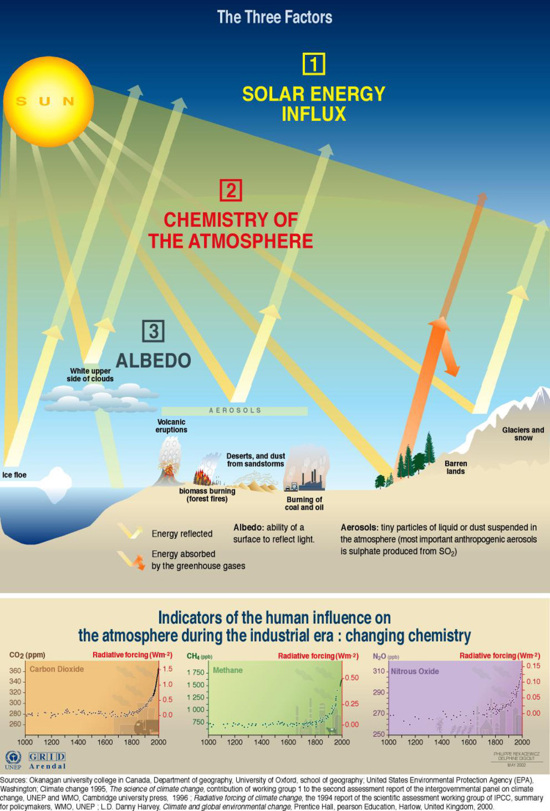



Factors Influencing The Greenhouse Effect Grid Arendal




Greenhouse Gases Quotes Quotesgram




The Greenhouse Effect Explained




Essay On Greenhouse Effect For Students 500 Words Essay
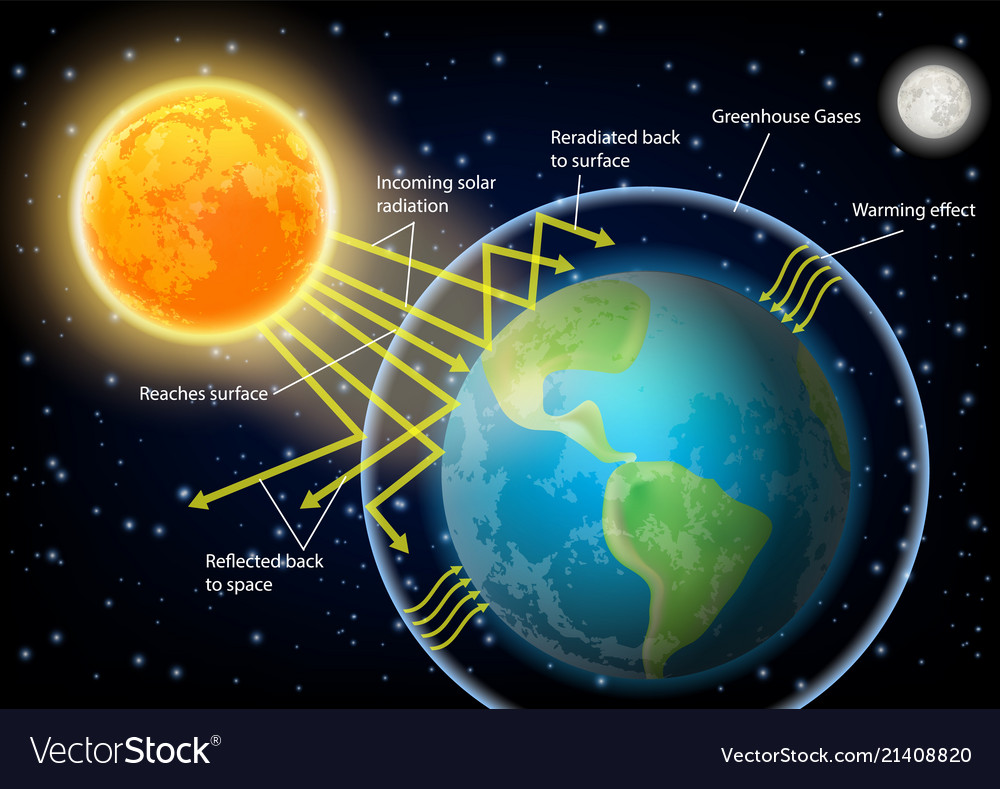



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Royalty Free Vector Image




Greenhouse Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
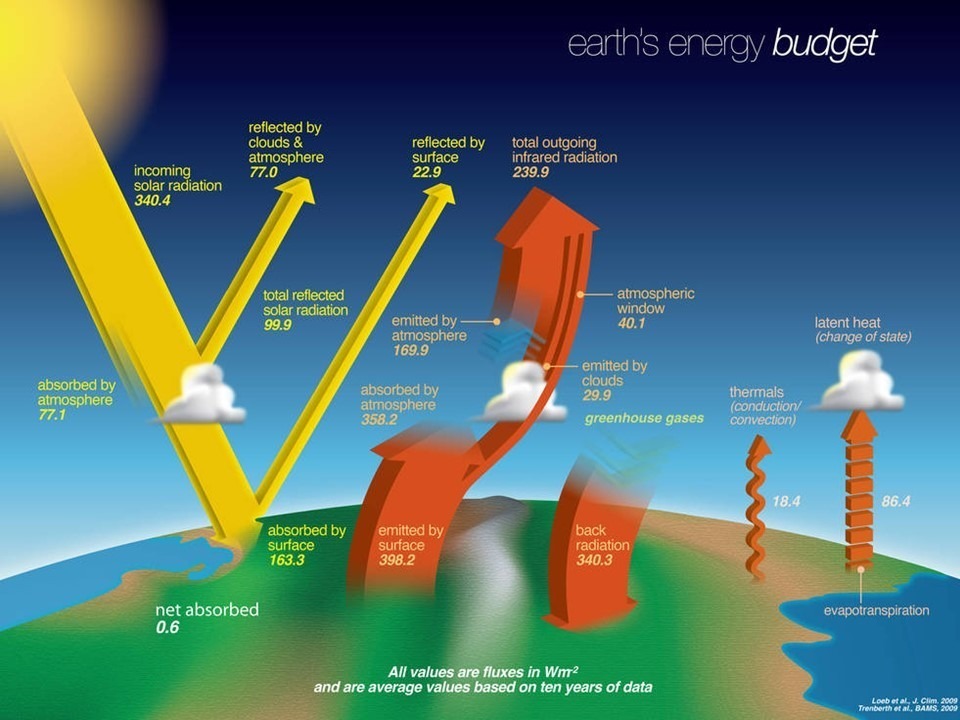



Comments On Dr Ollila S Claims That Greenhouse Effect Calculations Violate Energy Conservation Roy Spencer Phd




How To Draw A Diagram Of Green House Effect Global Warming Easy Youtube
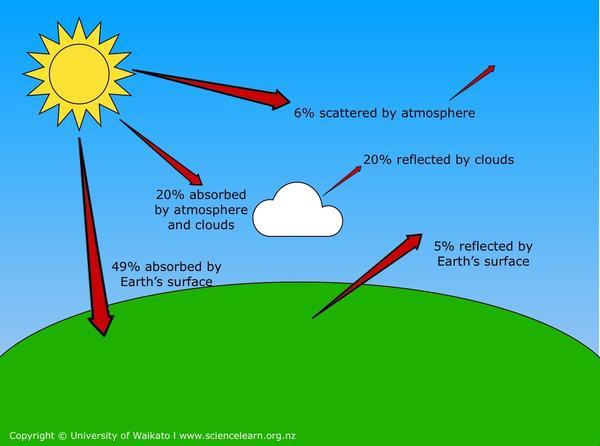



Greenhouse Effect Science Learning Hub




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa
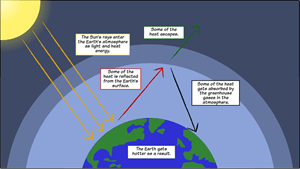



Creating A Greenhouse Effect Diagram




Why We Measure Track Ghgs Sustainable Practices The Office Of Sustainability Umass Lowell
コメント
コメントを投稿